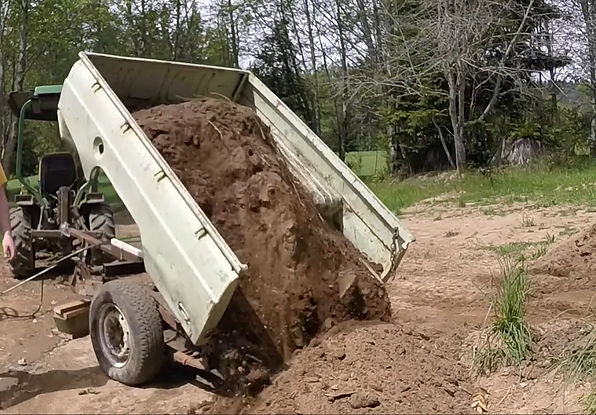
Dump Bed Lifiting Mechanism
Introduction
This project was motivated by a need to create a device that would cause a small truck or trailer bed to lift up quickly and dump its contents, eliminating the need to use manual physical labor, which is both slow and exhausting. This device will be incorporated into a homemade trailer and be engineered to lift up the surface of the dump bed to an angle sufficient to empty the contents consisting of dirt, rock, grass, wood or similar materials. The intended use for this device would be in a farm or similar setting where a minimal labor force is available. This project is being approached as a single individual, as his MET senior project. The majority of the effort for the individual will be in the design and analysis of the scissor arms. This will be the most critical part of the system. There will also be considerable effort in the machining and assembly necessary in the construction of the device. This project will consist of three areas, design, manufacturing and testing.
Analysis
-
Approach: The Analysis began with the need to calculate the necessary forces required to open the scissor lift burdened by the weight of the dump bed and its contents. Calculating the sum of the moments will accomplish this. After this force was determined, then the forces that are on the upper arm could be evaluated. In this particular project the majority of the analysis focuses on the upper scissor arm, this arm is the most critical and will determine if the load can be lifted.
-
Optimization: This device has been optimized to use a cylinder that has a bore size of 2 inches and stroke of 6 inches. Appendix A, Figure 5, shows the force necessary to open the dump bed with the determined geometry. Large cylinders that are commonly comprised of at least a 5 inch bore and a 20 inch stroke are expensive and must be placed into a stronger, larger more costly structure, as in Figure 2. This device is a smaller version that is similar to the previously discussed benchmark. By using a less expensive smaller cylinder, this new device will perform a similar function, in less space and be able to handle smaller loads, making it more manageable and safer.
-
Significant cost savings will be realized by using a small cylinder.The small cylinder can be obtained for around $70, while the cost of the large cylinder is over $400. Costs were obtained using information from SurplusCenter.com
-
Required Parameters: A minimum force of 2758 pounds is required to lift the load of 700 pounds at 31 inches. Reference Appendix A, Figure 5-7. The 700 pound load consists of 500 lbs. of material, 100 lbs. of the dump frame, and an added 100 lbs. by the moment. 2758 pounds was found by calculating the forces in each arm.
-
Calculated Parameters: In Appendix A, Figure 3, shows the estimated time it will take the lift to dump the load with a pump flow of two GPM. It accounts for 45 seconds for the load to be dumped out, and a total time of 49.29 seconds to lift, to dump, and to close. Figure 4 is the same calculation with a pump that has a decreased flow rate of .5 GPM. This should slow the process of lifting and closing and make the lift safer. Figure 8 shows the minimum pressure required to obtain the force of 2758 pounds is 879 psi. Figure 9 is showing the max load for the pin at 2758 pounds. Figure 10-15 is FEA done in SolidWorks showing the von Mises stress, displacement, and what the safety factor is for a load ranging from 2000 lbs. to 4000 lbs. on the upper lifting arm.
Construction
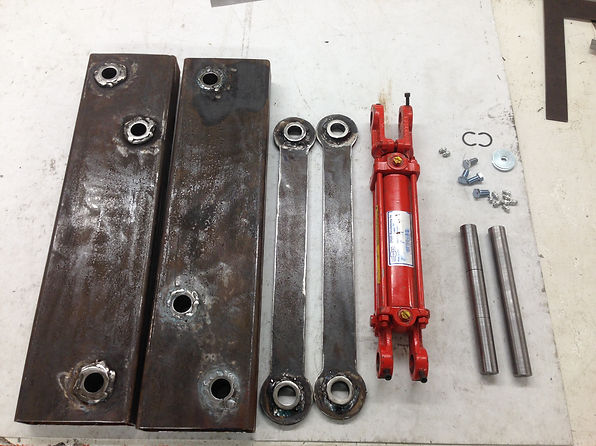
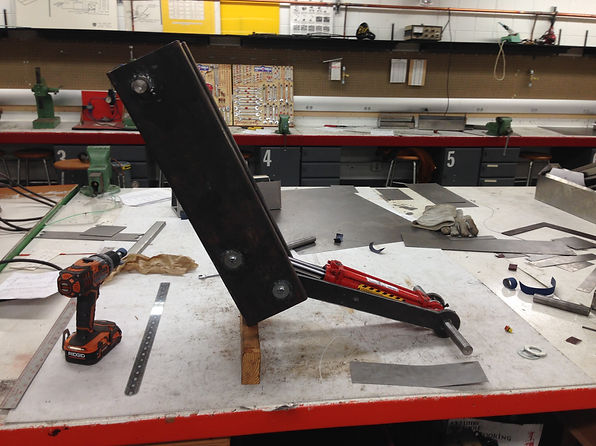
When the scissor lift is being constructed certain precautions will need to take place to maintain a precise part. The use of calipers, angle plate and other tools will help maintain the precision of the parts during measuring and assembly.
The use of the CWU machine shop, plasma table, and other resources will be used in this project to complete the project on time and on budget. Assembly of the scissor lift to the trailer frame and the dump bed will happen on location.


Testing
Introduction
In order to have a functional device there are several requirement to be fulfilled to determine if the device is successful. Test will be done to test the design requirements of the device that are listed on page 6. Hydraulic pressures will be in biggest interest in the tests. The calculated prediction with a .5 gpm pump is that it will take 62 seconds to lift 500 pound to lift, dump and lower the load. Data acquisition will be performed by recoding weight in bed, angle of lift, and pressure required to lift load. This testing will be done during April and May 2015.
Approach
To test the device adequate resources will be needed to perform the test. Testing will require 500 lbs. of material, a scale, a five gallon bucket, an iPhone with angle finder, a pressure gauge, hydraulic pump and a location to do the test. Data will be capture by video the process and recording the necessary values of the test like angle, PSI, and load. The device has an operational limit max pressure of 3000 PSI and should not exceed that incase of failure. Precision and accuracy will depend on the measuring equipment and repeating the tests enough time to get an average.
Test Procedure
The testing should be able to be completed within an hour, including set up and tear down. The test will be performed at the Novak Farm.
First load concert bags, four 80 pound bags and three 60 pound bags that equals 500 pounds, load it so it is centered on the bed. After the dump bed is loaded, turn on the hydraulic system and pull lever to lift the load. Measure angle at full lift, pressure to lift load, time to lift and lower load, and weight of load. Repeat four more times.
There should be very little risk in this test. The test is not exciting the maxim load of the device and should not fail. Safety is vary important in this test, the potential of lowering the bed onto an extremity could be possible. To keep everyone safe during the test communication needs to be present, before the lift is lifted operator needs to call out “lifting” and hear the ok to lift. The same thing needs to be present when lowering the lowed, operator calls out “lowering” and waits for the ok before lowering. A clear path around the trailer needs to be present to not cause any tripping hazards. The test will be considered successful if the load can be lifted and lowered.
Deliverables
There are five parameter that this test will be testing. They are size of the device, angle of tilt, achieve angle with six inch stroke cylinder, lift 500 pounds centered on dump bed, and lift with an input pressure of 1000 PSI. The test will be successful if the device can get to a 40 degree angle, use a stoke of 6 inches, lift 500 pound load under 1000 PSI. Reference Appendix H for results.
After testing the device it was able to lift 500 pounds centered on the bed with an input pressure of 1200 PSI. The calculated lifting pressure of 1000 PSI came from a bed weight of 100 pounds. With 200 more PSI required to lift the load then what was calculated was due to a under estimate of the bed weight which is closer to 250 to 300 pounds. The pressure to lift the bed with no load was 700 PSI. The angle achieve was 39 degrees and has a number of factors why it did not achieve 40 degrees, one was is that the mounting points of the device could be off by one inch and would have changed the angle by a degree. 39 degrees will be sufficient to dump a load and will not decrees the efficiency of the device.
Over all the testing was a success. The 1200 PSI to lift the load and bed was due to a under estimate of the bed weight, it only took 500 PSI to lift the load. With the angle being 39 degrees witch also pass the test and will be consisted successful.
Device Requirments
-
It must be compact. 26”x16”x12”
-
It must tilt a 6-foot bed to a 40º angle.
-
It must be able to lift a load with a cylinder with a maximum extension of 6 inches.
-
Must lift up to 500 pounds centered on the dump bed, located three feet from the hinge point.
-
Must be able to lift the load with an input Pressure of 1000 PSI or less.

Results
Test one
-
Size: 24"x14"x9". Meets the requirment.
-
Angle of tilt: 39º. This will meet the requirment beacuse its a cloese enough angle and having a error of +/- 1.



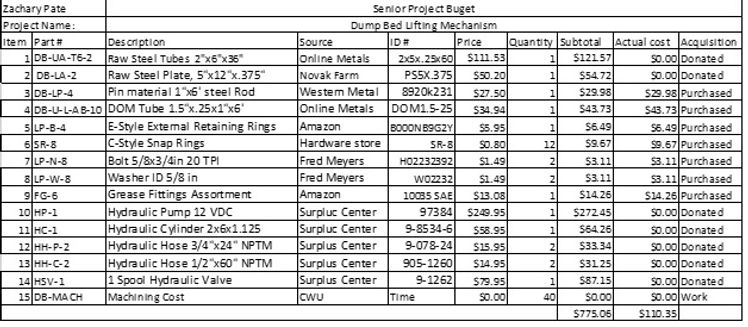
Budget
Schedule
-
Decmber - Proposal
-
January - Analyses
-
February- Part Construction
-
March - Device Assembly
-
April - Testinging
-
May - Evaluation
-
June - Deliverables
Conclusion
After testing the device it was able to lift 500 pounds centered on the bed with an input pressure of 1200 PSI. The calculated lifting pressure of 1000 PSI came from a bed weight of 100 pounds. With 200 more PSI required to lift the load then what was calculated was due to a under estimate of the bed weight which is closer to 250 to 300 pounds. The pressure to lift the bed with no load was 700 PSI. The angle achieve was 39 degrees and has a number of factors why it did not achieve 40 degrees, one was is that the mounting points of the device could be off by one inch and would have changed the angle by a degree. 39 degrees will be sufficient to dump a load and will not decrees the efficiency of the device.
Over all the testing was a success. The 1200 PSI to lift the load and bed was due to a under estimate of the bed weight, it only took 500 PSI to lift the load. With the angle being 39 degrees witch also pass the test and will be consisted successful.

